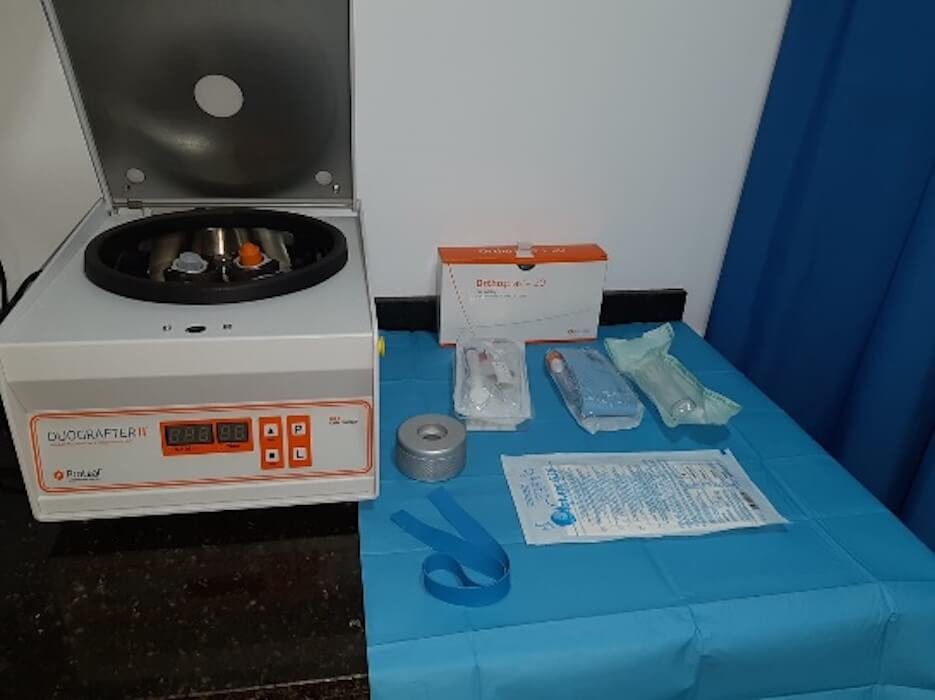
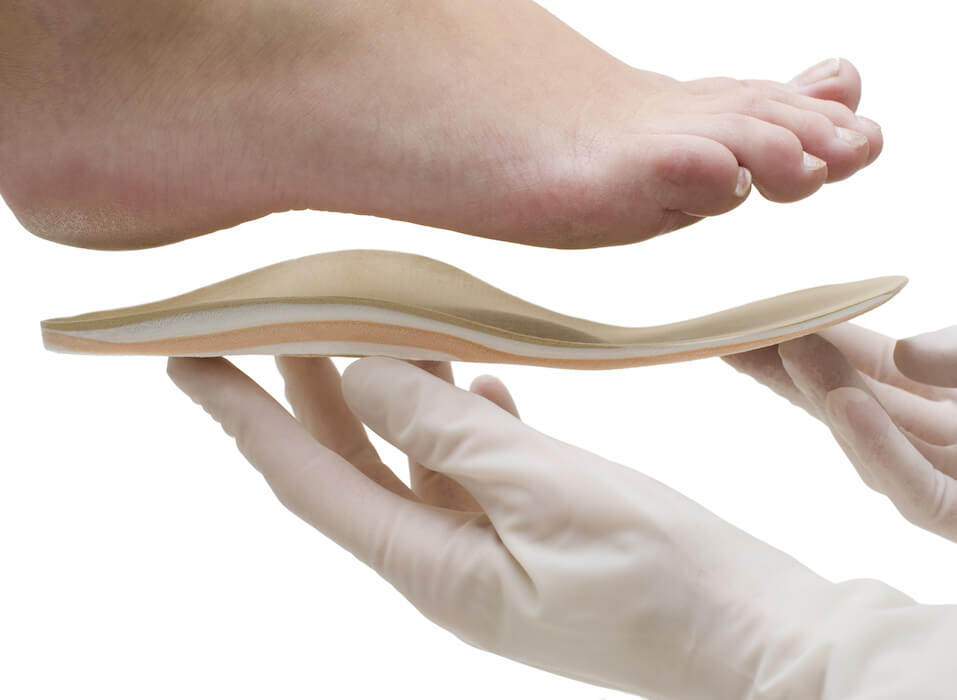
Bone and joint injuries are very common in the foot, including deformities, stress fractures, osteoarthritis, etc. This is because the foot is a very complex structure formed by 28 bones that join together forming multiple joints. The foot is governed by a very complex biomechanical system that deteriorates and deforms over the years by many factors, such as Diabetes, overweight, sports, genetic condition or the use of inappropriate footwear, among others .
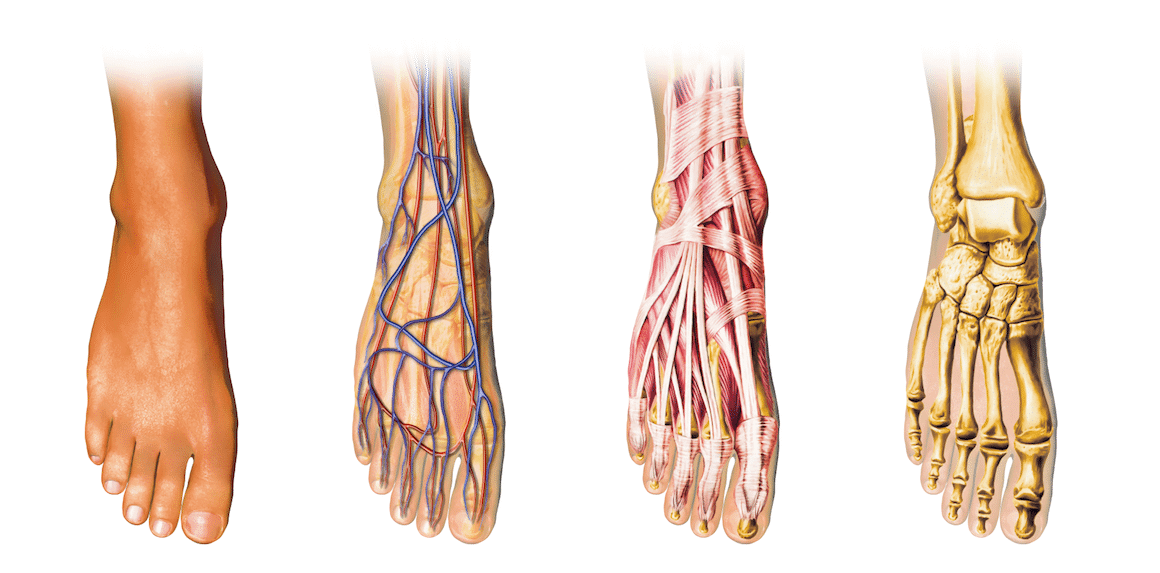
In the Podiatry Unit of the Clínica Vascular Marbella we carry out the diagnosis and correct treatment of dermatological, bone and joint injuries, soft tissue injuries (tendons, muscles and ligaments) and injuries of the peripheral nerves of the foot and ankle.
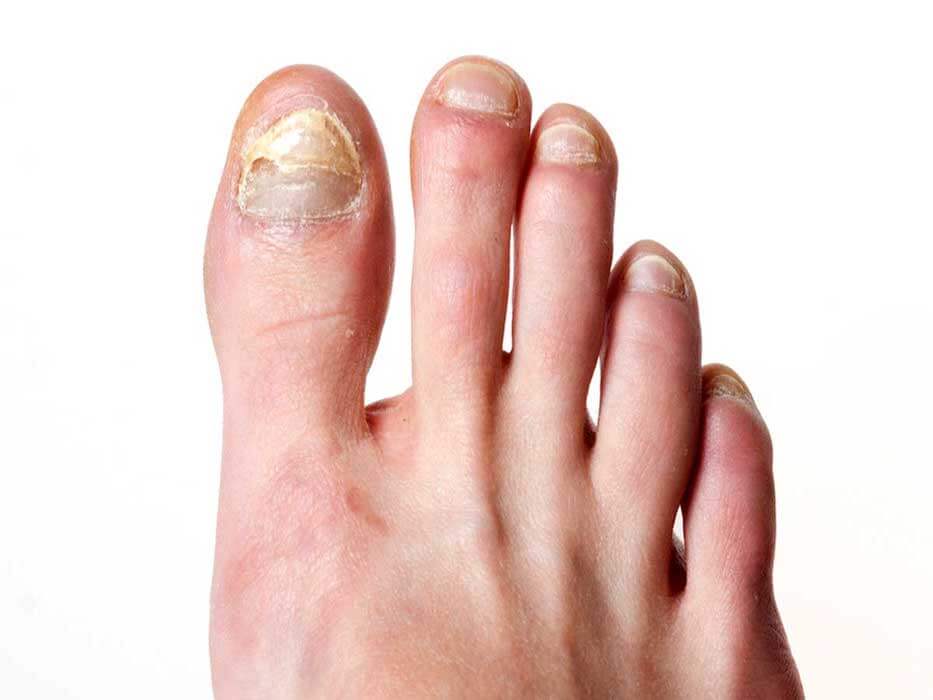
Mycosis (Athlete’s Foot)
It is the most common funfal infection in teenagers and adults, and is the classic illness of athletes and swimmers. Its most common cause is Trichophyton rubrum. This infection usually appears between the toes, nails and sole of the foot. It is presented as a desquamative process and subsequently there is a maceration of the skin due to fungal proliferation, causing color changes and a bad smell.
The treatment is usually topical by antifungal and hygienic measures that avoid the risk factors that feed the growth of microorganisms.
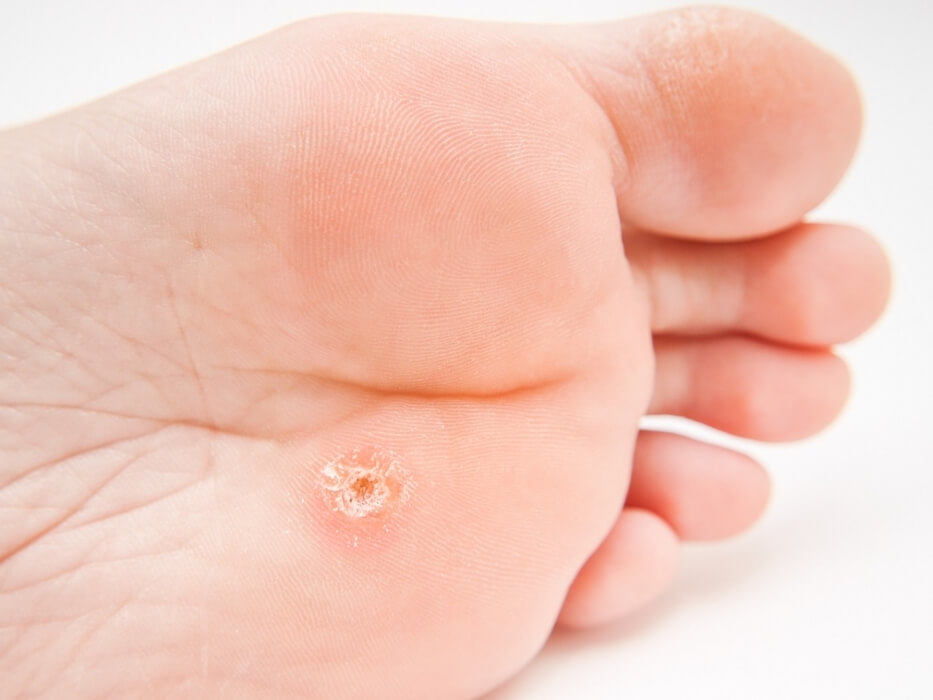
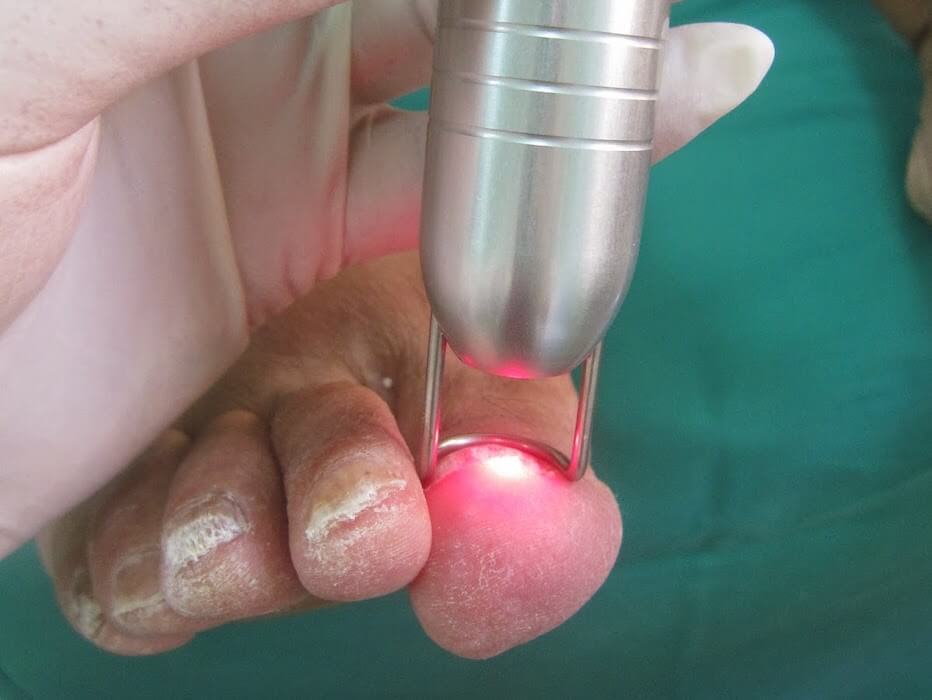
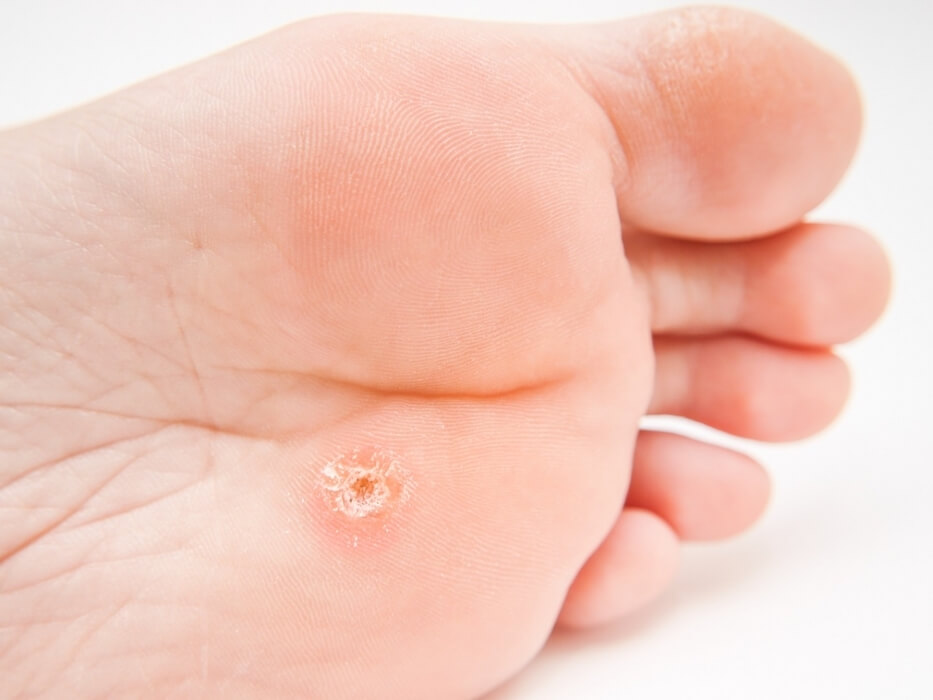
Viral diseases (papillomas or plantar warts)
Warts are very painful benign tumors, caused by the infection of keratinocytes of the epidermis by human papillomavirus (HPV). So far there are more than 100 known types of HPV and these determine the anatomical distribution and morphology of the lesion.
Papillomas are caused by infection and depend on several factors, as the location of the lesion or the patient’s immune status.
There are different patterns of papillomas and a good differential diagnosis must be made because it can be confused with other pathologies.
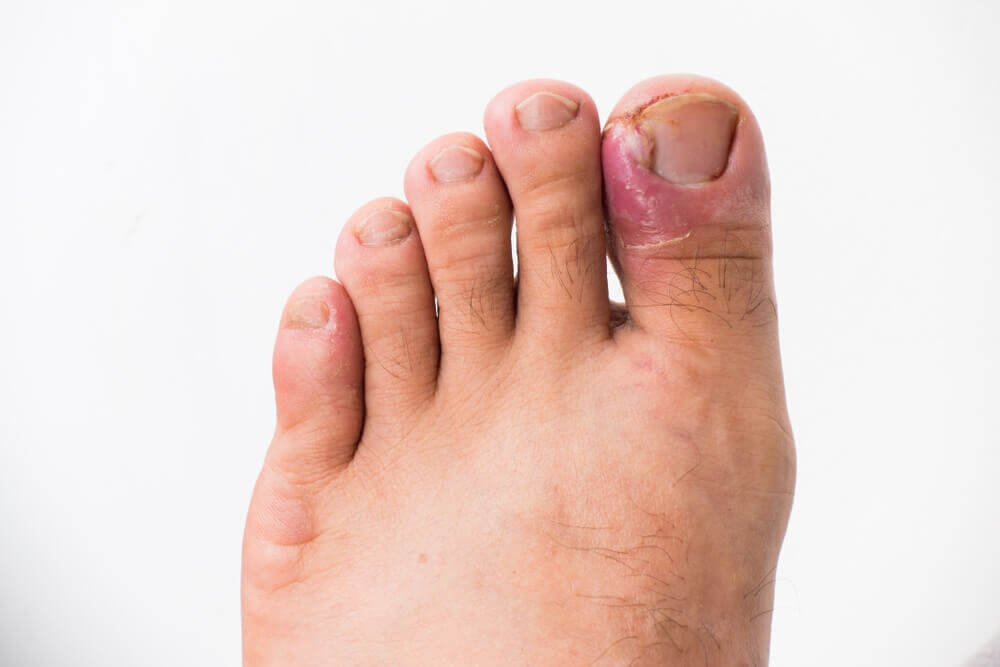
Ingrown toenails (ONICOCRIPTOSIS)
It is one of the most frequent pathologies in the feet, characterized by the injury that causes the lateral edges of the nail when it is trapped in the periungual grooves (around the nail), causing an inflammatory condition with frequent pain and infections.
Among the origin causes, the main ones are the use of an inappropriate shoe and an incorrect nail cut, although there are more predisposing factors.
In general, it is a chronic, unpleasant, painful pathology and significantly affects the life quality of those who suffer from it.
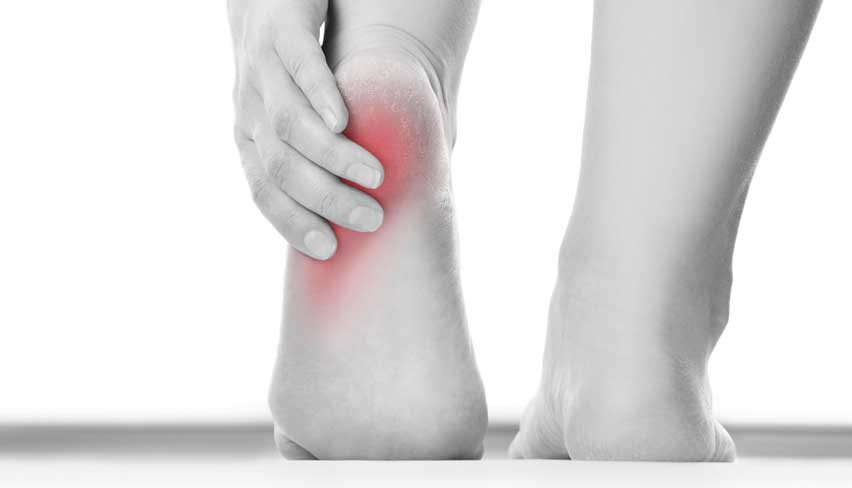
Plantar fasciitis
What is it?
The plantar fascia is a ligamentous structure responsible for cushioning impacts, redistributing loads and maintaining the arch.
Causes
- Obesity
- Running
- Long periods of standing time.
- Biomechanical factors: valgus rearfoot or decrease in ALI, dysmetrias, retraction of twins.
Symptomatology
It starts with a morning pain that appears after a long resting period , in the first steps of the morning and decreases with activity.
Diagnosis
It is valued based on pain, inflammation and other factors.
The fundamental test is the ultrasound of the foot as it give us a perfect view of the plantar fascia, how are its fibers and thickness.
The biomechanical study of the footprint is also fundamental in the diagnosis of this pathology.
Treatment
As a treatment, weight loss is recommended in overweight patients, adequate footwear, plantar support, cryotherapy, stretching of the gastrocnemius-soleo complex, and infiltrations.
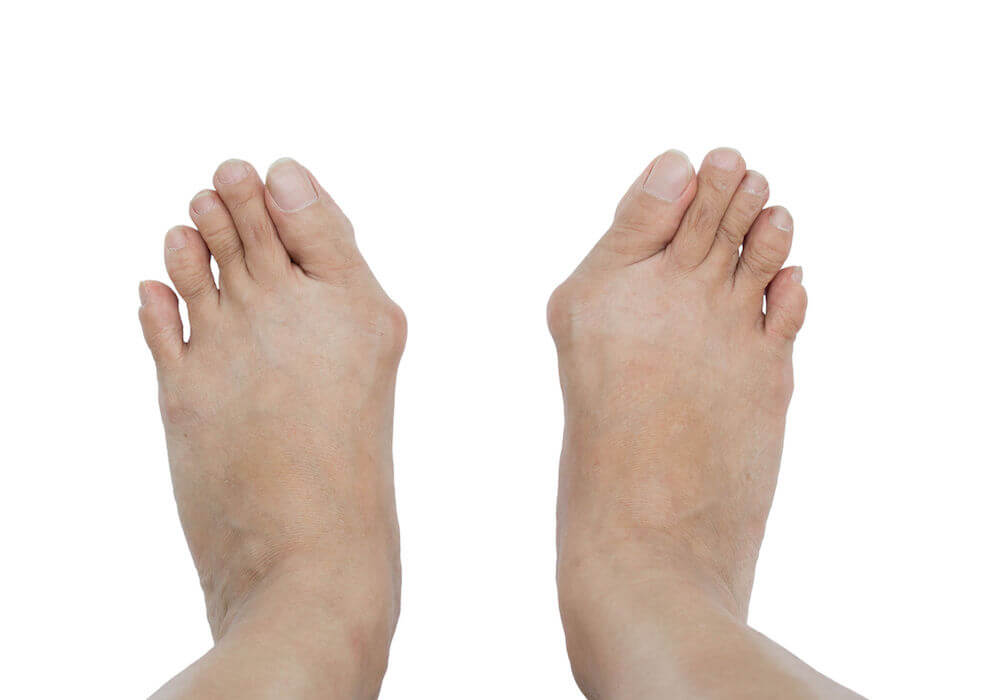
Bunions
What is it?
It is the most common bone deformity of the foot in the transverse plane, it is characterized by a deviation of the first metatarsal inward and the proximal phalanx outward, appearing a bony prominence called bunion.
Risk factors
There are several factors, they may appear due to genetic causes, inadequate narrow-toed shoes or biomechanical factors (hypermobility on the 1st radius, pronation of the foot, retraction of the Achilles).
Signs and symptoms
The most common signs are: overloads and poor support of the metatarsals, the tendon of the long extensor of the first finger is tense, the first finger occupies the space of the second and this gets a hammer toe shape, causing an increase in the metatarsal heads and pain.
The symptom is pain in the bunion, with redness and inflammation.
Diagnosis and treatment
The diagnosis is based on a biomechanical exploration and the conservative treatment will be the use of a wide footwear and plantar support.
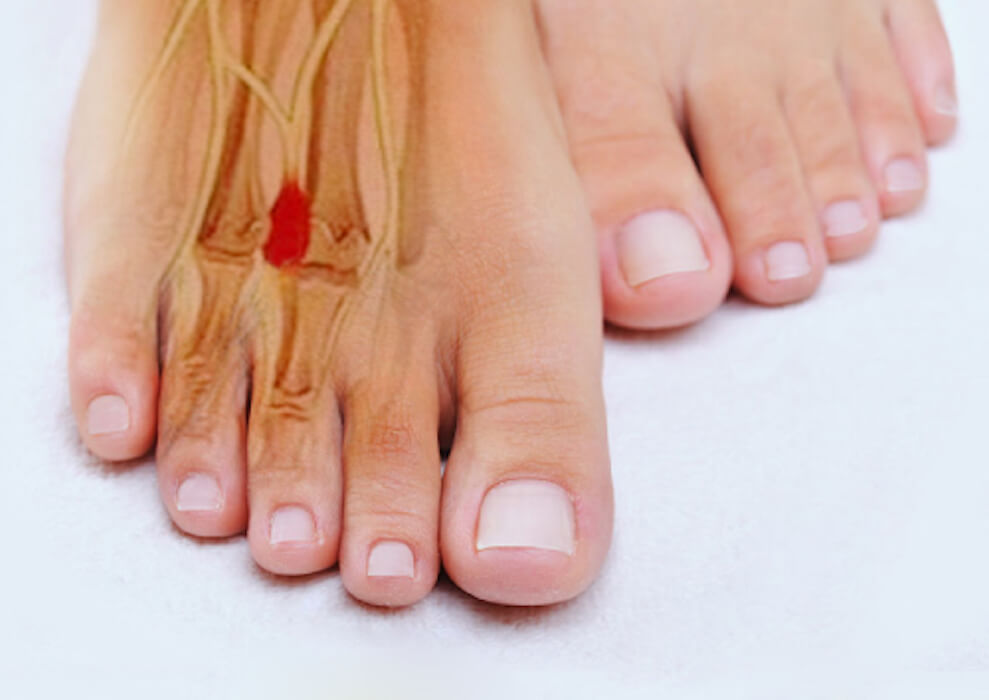
Morton’s neuroma
What is it?
Morton’s Neuroma is the thickening of the nerve that passes between the metatarsals.. t is caused by repetitive impacts against the ground or by little space between the bones of the foot that compress the nerve.
Causes
The main cause for the appearance of neuromas in the foot is the pressure in the metatarsal area due to an over-support of the forefoot, which causes friction between the nerve and the surrounding structures.
Symptomatology
The main symptom is pain, a pain that is described as if it were a sharp electric shock or a sensation of burning the foot area, tingling between the interdigital space of the third and fourth fingers, even preventing normal walking.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made through a sonography study along with an assessment of the footprint.
Treatment
Mild cases can be treated with custom insoles, in more advanced cases ecoguided infiltrations can be performed..

Plantar plaque lesions
What is it?
The glenoid plate is a structure located under the phalangeal metatarsal joint and its function is to stabilize the joint and prevent it from luxate.
Causes
The mechanism that causes damage is a consequence of repeated compressive loads along the metatarsal on the plantar plate. The insufficiency of the first radius due to a hallux valgus also causes instability of the 2AMTF.
Symptomatology
In the early stages pain appears in the forefoot, on the 2AMTF, which increases with walking and with edema at the base of the finger. In more advanced stages subluxation of the joint appears with a sign of a painful and reducible drawer. Once the pain is established, it passes to the plant, callus appears in the plantar area and deviation of the 2nd finger.
Diagnosis
A sonography diagnostic is made along with an assessment of the footprint.
Treatment
Infiltrations in pain phases, personalized plantar supports and silicone orthoses.
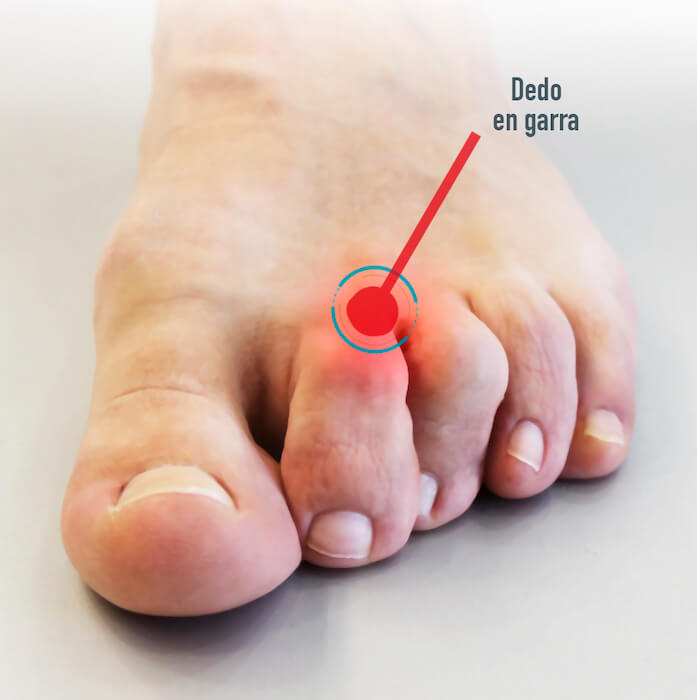
Claw fingers
What is it?
Claw fingers are a deformity of the toes that are shrunk due to a muscle imbalance, causing them not to rest on the floor and hurt.
Causes
The cause is due to many origins, but mainly due to an imbalance between the muscles and tendons that go above the fingers and the plantar area that they pull, retract and cause the claw toe.
Symptomatology
The main symptoms are calluses on the back of the fingers, on pulps, pain, and discomfort in the metatarsal heads because the finger does not rest on the ground and there is no adequate distribution of the loads.
Treatment
There are two options:
- Conservative, silicone prosthesis or plantar support.
- Surgical. Tenotomies, arthroplasties or arthrodesis.

Metatarsalgia
What is it?
Metatarsalgia is inflammation of the metatarsal heads due to poor distribution of pressures in the forefoot during walking.
The first metatarsal is the bone that must assume the greatest load, if this does not occur and the load passes to 2nd or 3rd metatarsal pain and inflammation occurs, since these bones are not prepared to assume so much weight.
Causes
- Index minus: first metatarsal shorter than the second.
- Claw fingers
- Achilles tendon retraction.
- Inappropriate shoe.
- Hallux valgus.
- Cavus foot.
Symptoms and signs
The main signs and symptoms are pain and burning and the appearance of hyperkeratosis in the pressure zones.
Diagnosis
Assessment through a biomechanical study of the footprint accompanied by an ultrasound study.
Treatment
- Wear appropriate footwear.
- Insoles
- Infiltrations
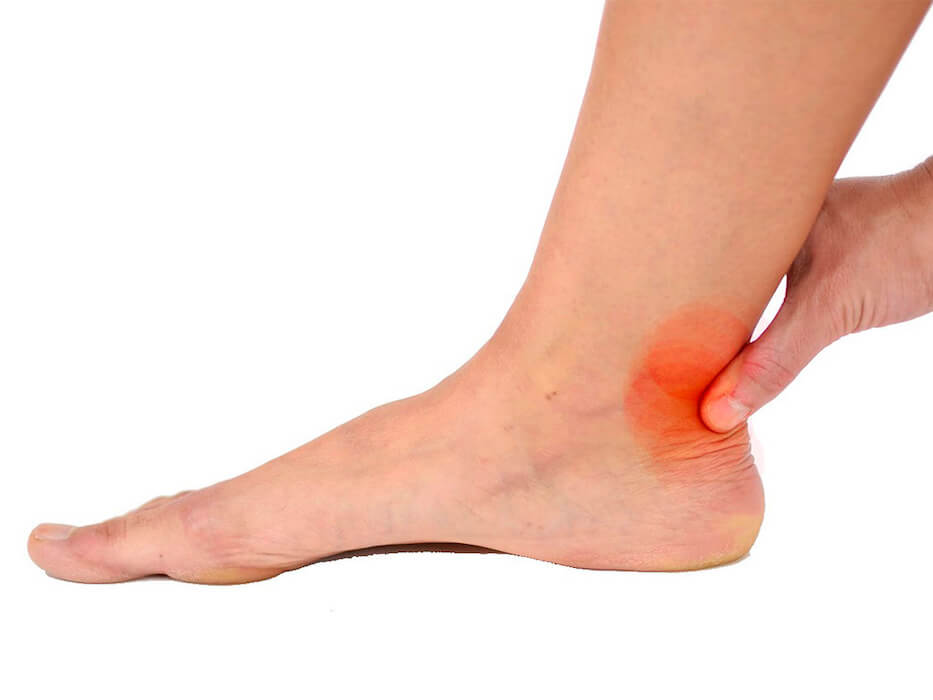
Achilles tendonitis
What is it?
Aquilea tendonitis is the inflammation of the Achilles tendon, sometimes it is associated with paratendinosis, inflammation of the sheath that covers the tendon (paratendon).
Causes
The origin of the lesion is multifactorial:
- Overweight
- Flat shoe or sports shoe with excess cushioning, that causes instability in the initial support of the walk.
- Walking or running long distances over soft terrain.
- Dysmetry
- Retraction of twins or hamstrings.
- Rheumatic diseases.
Symptoms
Morning pain that begins with the beginning of the activity, walking barefoot or with a flat shoe.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is based on the symptomatology and ultrasound imaging. It is important to do DD with Pre and retroaquilea bursitis, paratendon edema, Haglund disease, partial Achilles tendon rupture.
Treatment
Infiltrations with platelet-rich plasma and plantar supports to treat a valgus or unstable hindfoot or dysmetry and stretching of twins and hamstrings.
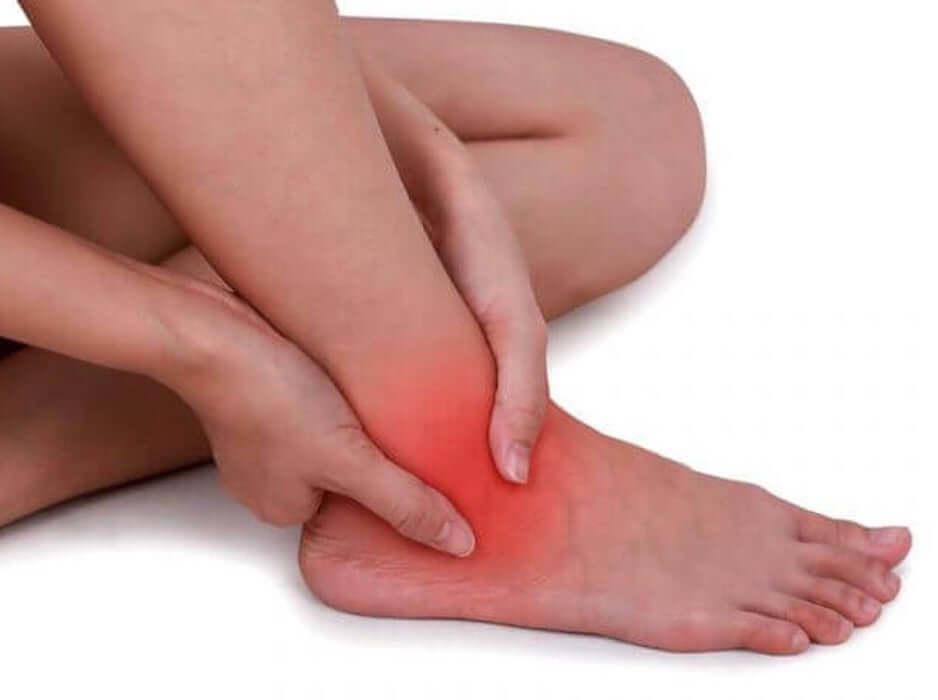
Posterior tibial dysfunction
What is it?
The posterior tibial originates from the posterior area of the tibia and fibula and is directed down and into the inner part of the ankle, becoming a tendon. This tendon is inserted into scaphoid and sends expansions to the first and second wedge and to the base of the second, third and fourth metatarsal.
Its function in load is to take the foot towards investment and plantar flexion. In cargo subject to the ALI in the medium support phase, controlling pronation and absorbing the impact against the ground.
Symptoms
TP dysfunction starts with edema, hyperalgesia, feeling of weakness and gradual loss of ALI.
Diagnosis
The sonography gives us information about the condition of the tendon and the biomechanical assessment of the footprint along with a series of FUNCTIONAL TEST.
Treatment
In early stages, plantar support to reduce posterior tibial tension, physiotherapy, cold, bandages and in more advanced stages infiltrations.
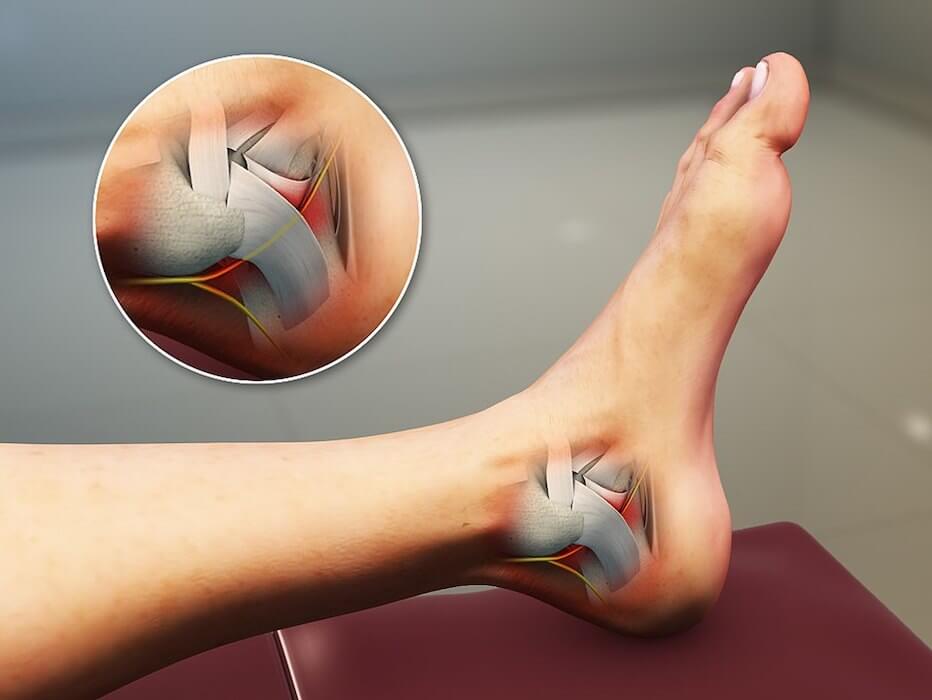
Tarsus tunnel syndrome
What is it?
The posterior tibial nerve runs through the internal part of the heel and its branches give sensitivity to the internal part of the heel and part of the sole of the foot. Patients who turn their feet inward, who have some muscle deficit or some narrowing of the canal through which the nerve passes and can be compressed are more likely to suffer from this disease.
Symptoms
Pain in the heel area that appears when we rest after the day. Pain may also appear in the inner ankle area that radiates to the sole of the foot.
Diagnosis
A physical examination, ultrasound and biomechanical study of the footprint will be performed.
Treatment
Ecoguided infiltrations and custom insoles to prevent harmful movements that may be causing this injury.
When the child begins to walk the foot has a flat appearance with a lot of fatty tissue on the sole. That is completely normal. With 2 years, the foot begins to show its appearance in a more characteristic way, if the child presents a flat foot deformity at that age, it is essential that I go to a podiatry specialist. In this way we can achieve a definitive correction of it. Plantar supports must be used in children always in justify cases, taking into account the specialized diagnosis.
Normally it is from the age of 10 when the body of the child begins to accuse the problems that have not been detected and treated in childhood, hence the importance of attending and treating these pathologies preventively.
What pathologies are the most common in children?
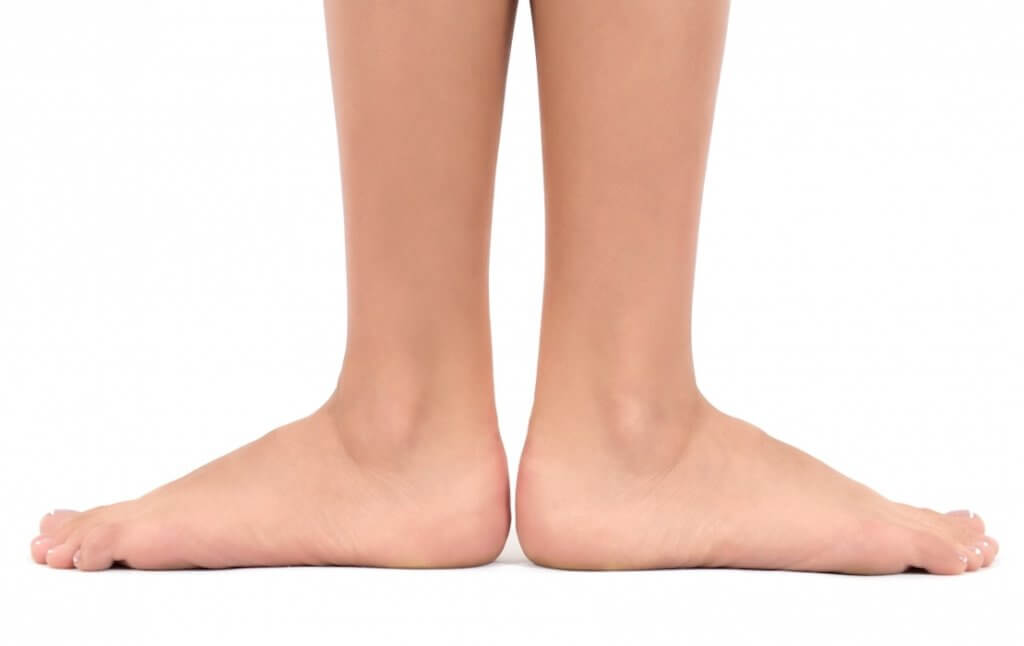
Flatfoot
When we talk about flat feet we refer to the decrease in the internal arch of the foot, giving a flattened appearance.
If after 3 years of age the foot muscles are not able to form a plantar arch, it is recommended to start with an orthopodolological treatment accompanied by shoe therapy.
Heel pain (Sever’s disease)
This pathology consists in the inflammation of the calcaneal growth cartilage. It is characterized by a pain that appears at the heel level especially when performing physical activities. It is usually one of the most common causes in children between 8 and 13 years.

Walking with feet inward
It consists of a deviation into the anterior part of the foot. It may be due to one or several rotations of the lower limb, from the hip to the foot or it may also be due to postural habits.
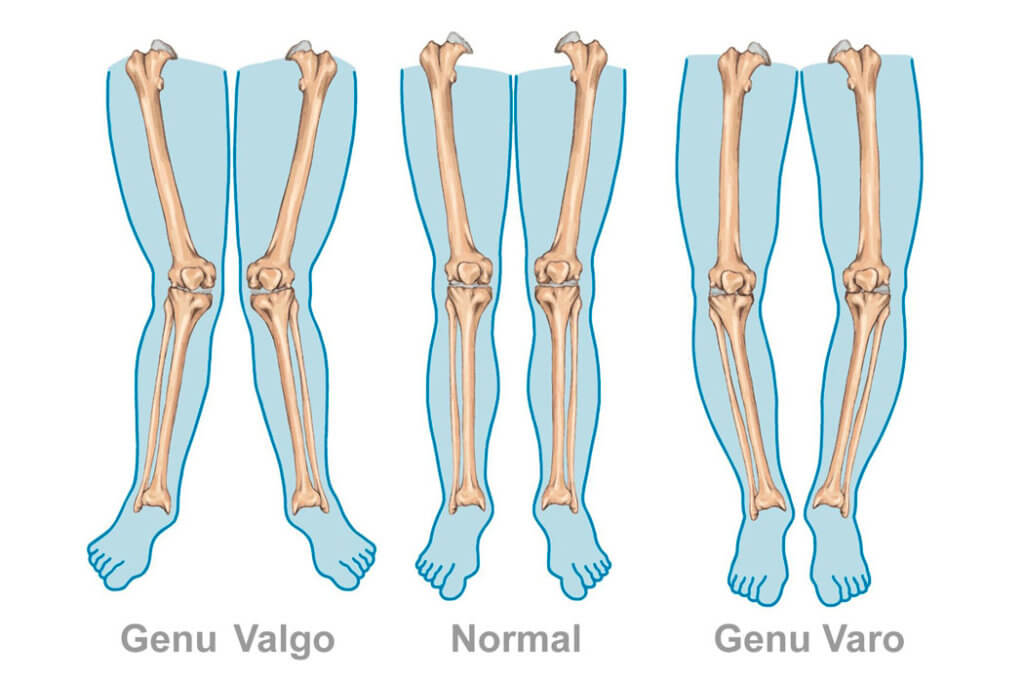
X knees. Genu Valgum
The genu valgum consists of an alteration of the angle formed by the legs seen from the front, in which the knees meet and the ankles are separated.
All children, pass a phase of physiological genu valgum, from 2 years, and between 3 and 5 in an accentuated manner, and up to 7 years, which is when the normal alignment is acquired.
Arched knees. Genu Varum
It consists of an inwards deviation of the anterior part of the foot. It may be due to one or several rotations of the lower limb, from the hip to the foot or it may also be due to postural habits.